

The BESIII Collaboration has achieved a milestone in hyperon physics by performing the most precise test of CP symmetry and polarization analysis in Σ+ decays to date. The results have been published in Physical Review Letters on Oct. 1, 2025 [Phys. Rev. Lett. 135, 141804 (2025)].
Charge-parity (CP) violation is one of three essential conditions proposed by Sakharov to explain the dominance of matter over antimatter in the Universe. While the CP violation has been observed in several decays, the Standard Model described by the Kobayashi-Maskawa mechanism is insufficient to account for the observed matter-antimatter asymmetry. Therefore, it is crucial to search for new sources of CP violation, particularly in the hyperon sector.
Based on 10 billion J/ψ and 2.7 billion ψ(3686) events collected with the BESIII detector, the five-dimensional angular analysis of the processes of J/ψ and ψ(3686) → Σ⁺ Σbar-(Σ⁺→ pπ⁰,Σbar-→ pbar π⁰) has been performed. This study provides the first precise test of CP symmetry in the Σ⁺→pπ⁰ decay process. The results are consistent with CP conservation, with measurement precision improved by a factor of three to four compared to previous results. Additionally, the most precise measurement of the average decay parameter is obtained in baryon decays to date.
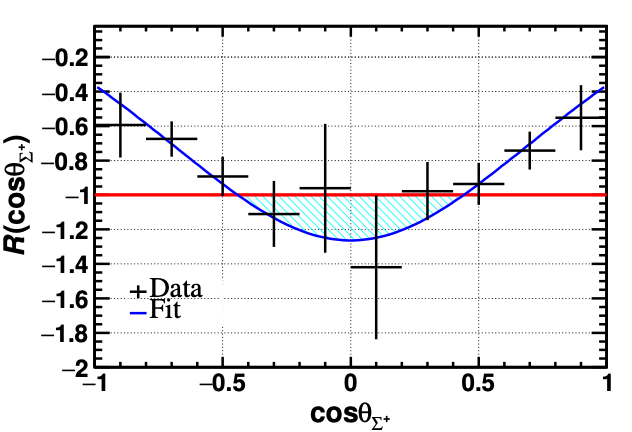
Figure 1 Polarization ratio between J/ψ and ψ(3686) decays as a function of Σ+ scattering angle.
The research also revealed unique polarization characteristics of Σ⁺ hyperons in J/ψ and ψ(3686) decays. Σ⁺ exhibits a sign reversal in polarization direction as shown in Fig. 1. Based on the covariant L-S theoretical framework, the S-wave/D-wave coupling ratio, relative phase, and the effective interaction radius of Σ hyperons are determined. These measurements provide essential constraints for understanding hyperon dynamics and the search for excited baryons.
URL: https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/ysd5-s2gn
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/ysd5-s2gn